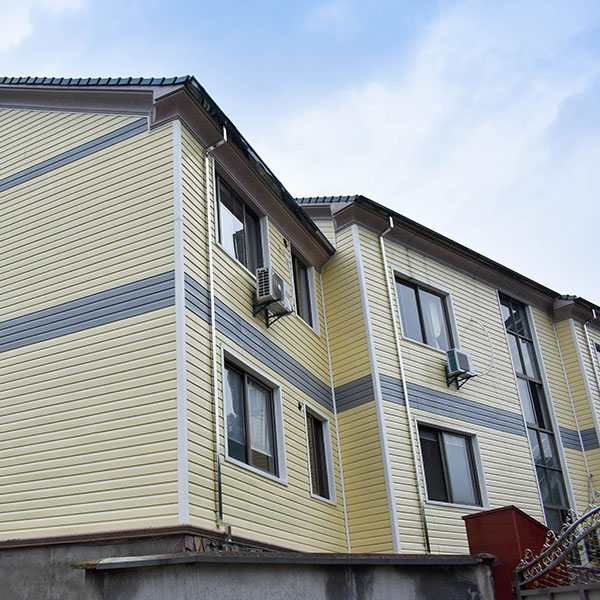
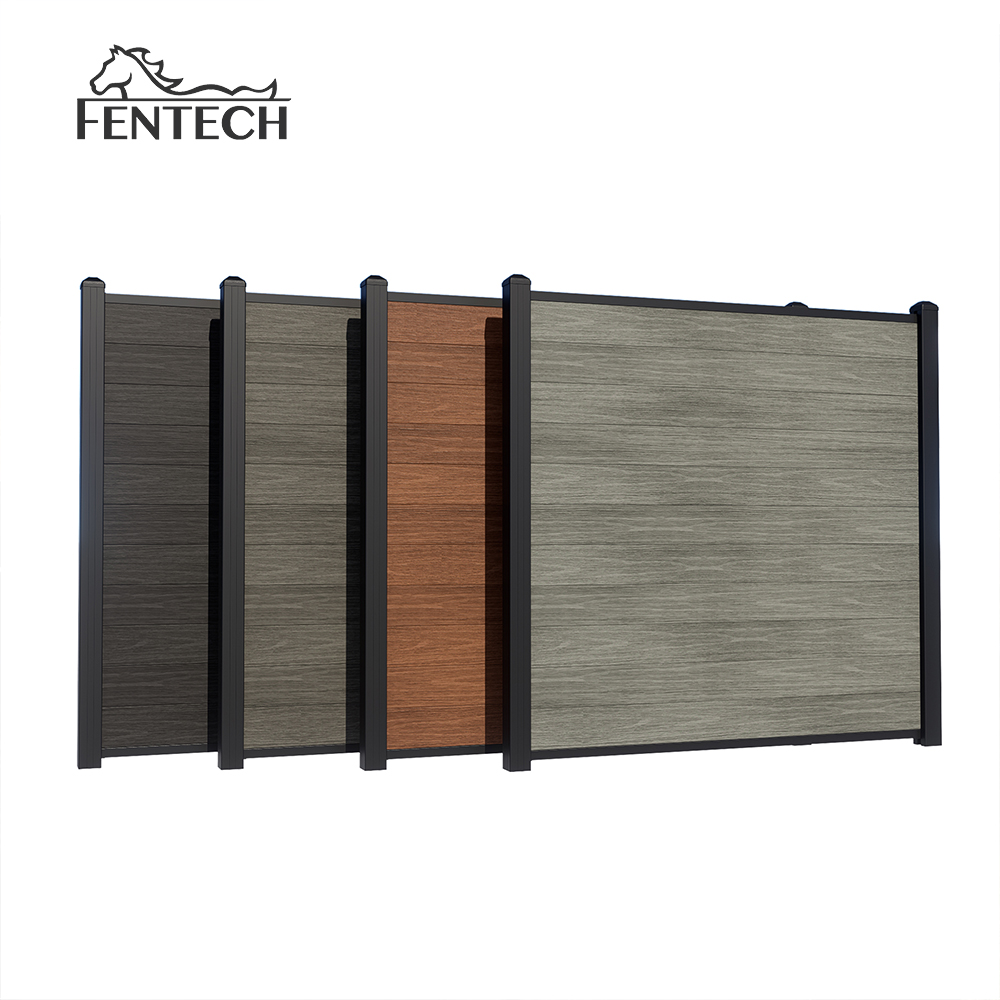
We are professional China Custom Vinyl Fence Manufacturers with fences virgin PVC/Vinyl material and UV Protected.
Outdoor living spaces have become an extension of the home, offering a place to relax, entertain, and enjoy the open air. With this growing focus on outdoor environments, the materials used to build decks are under more scrutiny than ever before. Homeowners want options that not only look attractive but also stand the test of time without requiring constant upkeep. Among the available choices, polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, decking has gained attention for its ability to withstand common challenges that often shorten the life and beauty of traditional wood decks.
One of the most appealing aspects of PVC decking is its resistance to three major enemies of outdoor surfaces fading, stains, and moisture. Each of these problems can quickly turn a once beautiful deck into a worn and unattractive surface. Understanding how PVC decking overcomes these issues provides insight into why it has become a trusted solution for long lasting outdoor flooring.
The Science Behind PVC Decking
PVC decking is made from synthetic materials rather than natural wood fibers. It is composed primarily of polyvinyl chloride, a durable thermoplastic polymer used in countless construction applications. Because it contains no organic material, it is naturally resistant to decay, rot, and insect damage. This sets the stage for its ability to resist environmental wear and tear.
While traditional wood decking absorbs moisture, fades in sunlight, and stains easily, PVC decking is engineered to minimize these vulnerabilities. Its solid composition, protective surface coatings, and non porous structure all work together to preserve its appearance and functionality over time.
Why Fading Happens in Outdoor Materials
Before exploring how PVC resists fading, it helps to understand why fading occurs. Outdoor materials are exposed to ultraviolet UV radiation from sunlight. These rays break down the chemical bonds in many materials, causing colors to fade and surfaces to lose vibrancy. Natural wood, in particular, is prone to bleaching and discoloration as UV light damages lignin, a component that holds wood fibers together.
Even composite decking, which blends wood fibers with plastics, can show some degree of fading over time because it still contains organic material that reacts to UV rays. This is where PVC offers an advantage.
How PVC Decking Resists Fading
PVC decking is designed with built in UV resistance. Manufacturers add stabilizers and pigments that help shield the material from the degrading effects of sunlight. These additives work by absorbing or reflecting UV rays before they can cause chemical breakdown in the surface layer.
In addition, PVC is often capped with a protective surface layer that provides an extra barrier against fading. This capstock technology ensures that even with prolonged sun exposure, the deck retains much of its original color and finish.
Because the color is integrated into the material rather than applied as a surface coating, scratches or wear do not expose lighter or unfinished layers beneath. This uniformity helps maintain a consistent appearance even as the deck ages. While no outdoor material is completely immune to the effects of long term sun exposure, PVC decking demonstrates a much slower and less noticeable rate of fading compared with wood or composites.
The Challenge of Stains on Outdoor Decks
Outdoor decks are often the center of activity. Food, drinks, plant matter, and other elements regularly come into contact with the surface. With wood, porous fibers absorb these substances, leading to stubborn stains that can be difficult to remove. Even with sealants and protective coatings, stains often seep into wood grain over time.
Composite decking, though less porous than wood, can still absorb certain oils or tannins, especially if spills are not cleaned promptly. This leads many homeowners to seek a decking material that is easier to maintain.
How PVC Decking Resists Stains
The non porous nature of PVC makes it highly resistant to stains. Unlike wood fibers, PVC does not absorb liquids. Spilled wine, sauces, or oils remain on the surface rather than seeping in. As a result, stains can usually be wiped away with a cloth and mild soap.
The protective cap layer further enhances this resistance by adding a slick, closed surface that prevents particles from embedding themselves. Even substances like grease or tannins from fallen leaves can typically be removed with simple cleaning.
In addition, PVC does not react chemically with many staining agents. Where wood might darken after contact with iron rich water or certain chemicals, PVC maintains its original color. This combination of non porosity and chemical stability gives PVC decking a practical advantage for homeowners who want a low maintenance outdoor surface.

The Problem of Moisture in Outdoor Decking
Moisture is perhaps the most destructive force for traditional wood decking. When wood absorbs water, it swells and contracts as it dries, leading to warping, cracking, and splintering. Persistent moisture also creates an ideal environment for mold, mildew, and rot.
Even composite decking, which blends plastic with wood fibers, can be vulnerable to moisture related issues. The wood content still absorbs water, leading to swelling, fungal growth, and surface spotting in damp climates. This is a major reason why homeowners in humid or rainy regions look for alternatives.
How PVC Decking Resists Moisture
Because PVC decking is made entirely of plastic, it contains no organic fibers to absorb water. This makes it virtually impervious to swelling, rotting, or decay. The closed cell structure does not allow moisture to penetrate, which eliminates many of the problems that plague wood based decking materials.
In addition, the surface of PVC is resistant to mold and mildew growth. While spores may still land on the surface, they cannot feed on the material itself. Simple cleaning with water and a mild detergent typically removes any buildup without permanent staining.
This moisture resistance makes PVC decking particularly well suited for areas near pools, hot tubs, or coastal regions where decks are exposed to frequent water contact or high humidity levels. It also reduces the need for repeated sealing or water repellent treatments that are common with wood decking.
Longevity and Maintenance Benefits
The combination of resistance to fading, stains, and moisture translates into a decking material that requires less upkeep over its lifespan. Traditional wood decks demand frequent sanding, staining, and sealing to maintain appearance and durability. Composite decks require less work but may still need periodic treatments or deep cleaning.
PVC decking, by contrast, generally requires only occasional washing with soap and water to keep it looking fresh. There is no need for refinishing or protective coatings. Over years of use, this reduced maintenance can save both time and money while ensuring the deck continues to look appealing.
Environmental Considerations
Another factor worth considering is how PVC decking performs in relation to environmental challenges. Because it resists fading, it does not require chemical stains or paints for color renewal. Its stain resistance reduces the need for harsh cleaners. And its resistance to moisture minimizes the use of preservatives or fungicides.
While PVC is a synthetic material and not biodegradable, many products are recyclable at the end of their useful life. For homeowners concerned about long term sustainability, checking whether the manufacturer offers recycling options is a practical step.
A Balanced Perspective
It is important to note that while PVC decking offers many advantages, no material is perfect. Its surface can become hot under direct sunlight, which may affect comfort in certain climates. It may also be more expensive initially than some wood options. However, when evaluating cost over the long term, the reduced maintenance and extended lifespan often balance the initial investment.
By understanding both the benefits and potential drawbacks, homeowners can make informed decisions about whether PVC decking is the right choice for their outdoor living space.
Conclusion
Decking materials must endure constant exposure to sun, spills, rain, and humidity. For many years, wood was the default choice, but it often struggled against fading, stains, and moisture related damage. PVC decking emerged as a solution engineered specifically to resist these challenges.
Its resistance to fading comes from built in UV stabilizers and protective cap layers. Its stain resistance is due to a non porous surface that repels liquids and prevents discoloration. Its moisture resistance stems from its all plastic composition, which does not absorb water or provide a food source for mold and mildew.
These qualities not only preserve the visual appeal of a deck but also reduce maintenance demands. While PVC decking is not without limitations, its performance in resisting the three major enemies of outdoor surfaces makes it a durable and practical choice for homeowners seeking long term value.
 English
English  中文简体
中文简体